James Webb Space Telescope
https://www.space.com/james-webb-space-telescope-micrometeoroid-damage
They're talking Nanometers. For perspective, 1 gold atom has an atomic diameter of 0.292nm. So, the original 56nm, is like 192 gold atoms in a line.
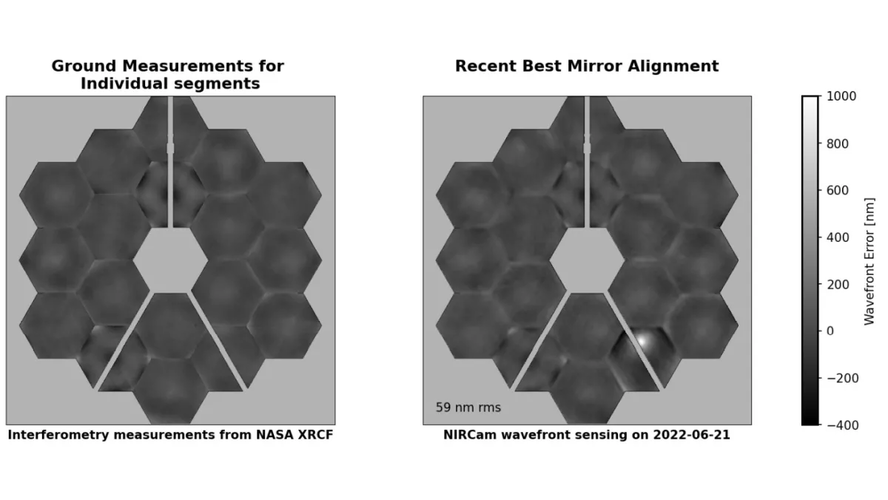
This gets into the details
https://www.space.com/james-webb-space-telescope-micrometeoroid-damage
They're talking Nanometers. For perspective, 1 gold atom has an atomic diameter of 0.292nm. So, the original 56nm, is like 192 gold atoms in a line.
