- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,167
- Reaction score
- 45,669
Offline
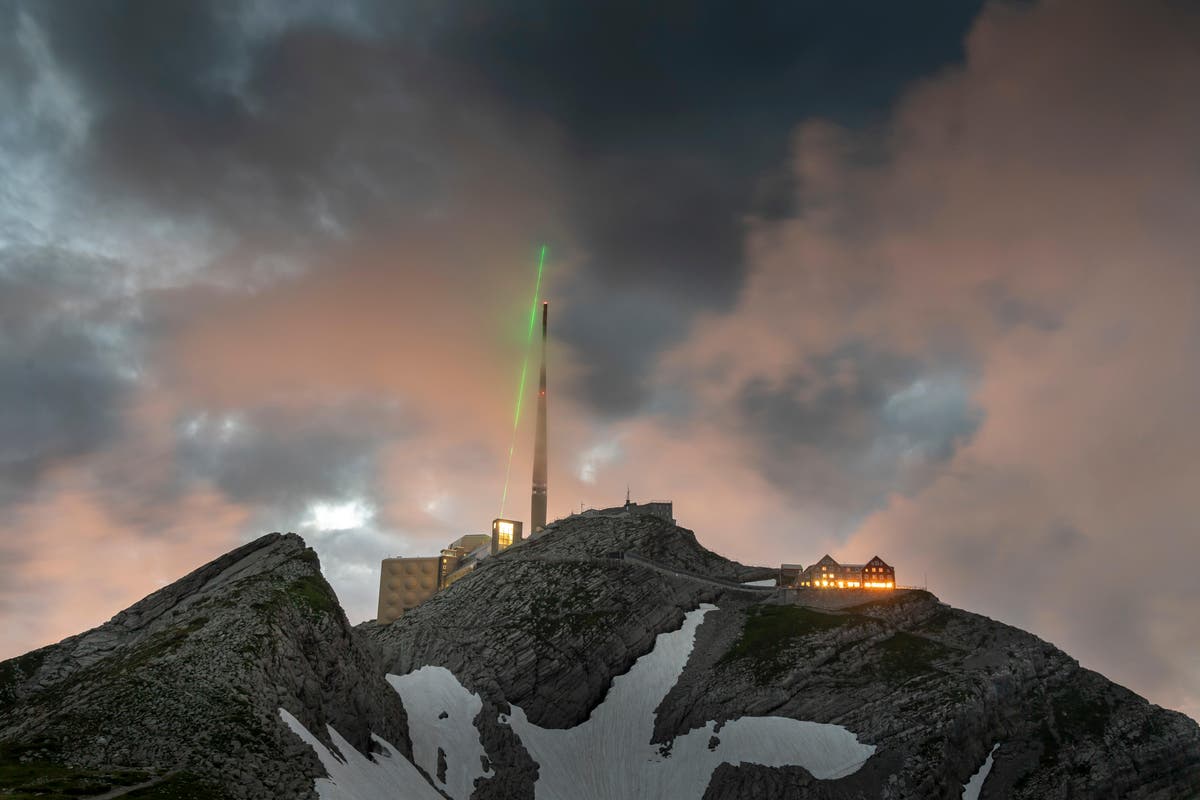
Scientists have demonstrated in a first that a powerful laser beam directed at the sky can create a “virtual lightning rod” that can divert the path of lightning strikes.
The research, published on Monday in the journal Nature Photonics, may lead to improved lightning protection methods for critical infrastructure like power stations, airports, and launchpads.
Until now, the most commonly used lightning protection device is the Franklin rod, which is an electrically conducting metal pole on top of buildings and other infrastructure that intercepts lightning discharges and guides them safely to the ground, scientists, including those from Ecole Polytechnique in France, explained.
In the new study, they showed that a powerful laser beam directed at the sky could act as a virtual, movable rod and offer an alternative……

 www.independent.co.uk
www.independent.co.uk
The research, published on Monday in the journal Nature Photonics, may lead to improved lightning protection methods for critical infrastructure like power stations, airports, and launchpads.
Until now, the most commonly used lightning protection device is the Franklin rod, which is an electrically conducting metal pole on top of buildings and other infrastructure that intercepts lightning discharges and guides them safely to the ground, scientists, including those from Ecole Polytechnique in France, explained.
In the new study, they showed that a powerful laser beam directed at the sky could act as a virtual, movable rod and offer an alternative……

Scientists use laser beam to guide lightning strike in a first
Laser increased radius of the protection surface from 120m (390ft) to 180m (590ft)