- Joined
- Jul 18, 1998
- Messages
- 22,159
- Reaction score
- 45,623
Offline
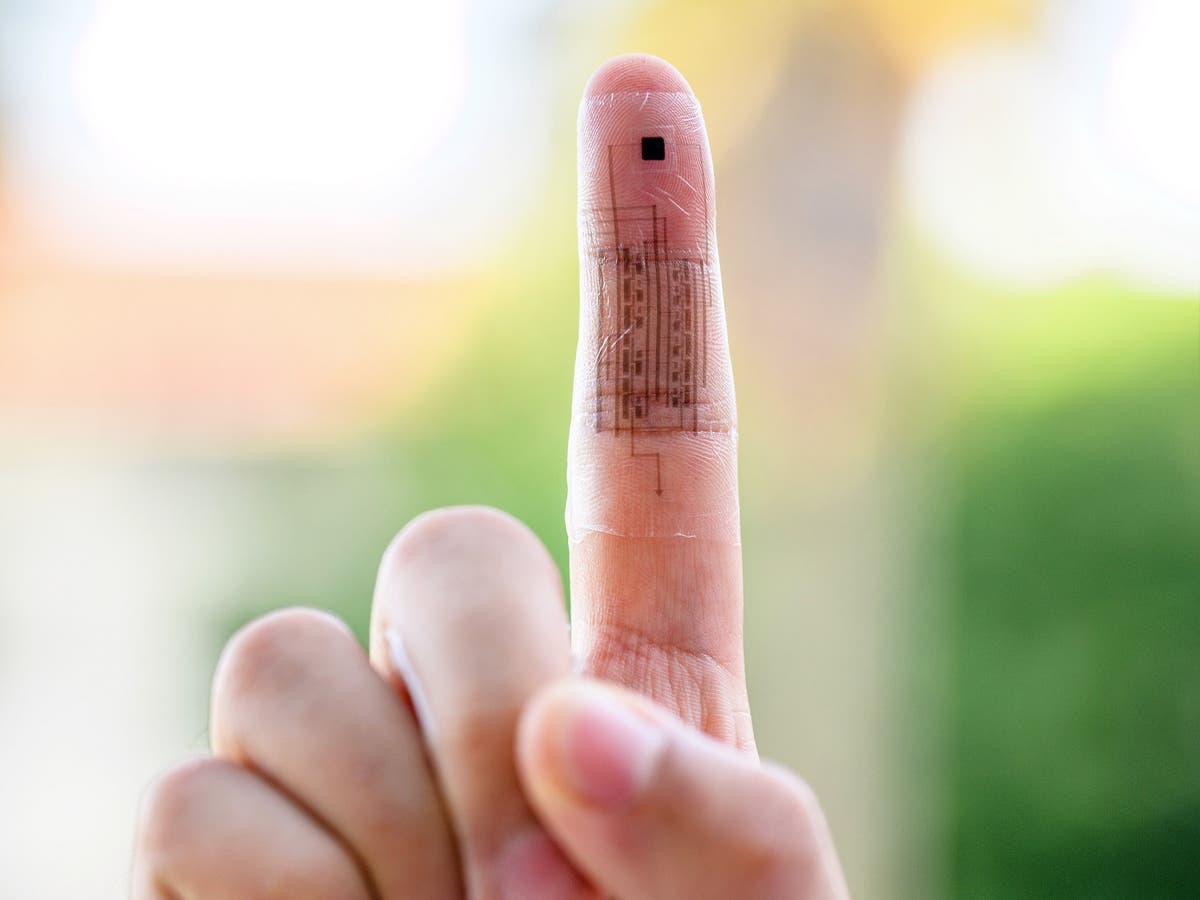
Scientists have invented a type of electronic skin that can “talk directly to the brain”, allowing amputees to feel a human-like sense of touch through prosthetic limbs.
The ground-breaking artificial skin is embedded with sensors for temperature, pressure and strain, which are converted into electrical signals – similar to how nerve impulses communicate with the brain.
The wearable electronic circuit, known as a monolithic e-skin, was developed by a team from Stanford University, who detailed their breakthrough in a study published in the journal Science.
Stanford University’s Zhenan Bao, who was a senior author of the study, told The Independentthat the next-generation technology could also be used to feel objects and sensations while controlling a robotic limb remotely…….

 www.independent.co.uk
www.independent.co.uk
The ground-breaking artificial skin is embedded with sensors for temperature, pressure and strain, which are converted into electrical signals – similar to how nerve impulses communicate with the brain.
The wearable electronic circuit, known as a monolithic e-skin, was developed by a team from Stanford University, who detailed their breakthrough in a study published in the journal Science.
Stanford University’s Zhenan Bao, who was a senior author of the study, told The Independentthat the next-generation technology could also be used to feel objects and sensations while controlling a robotic limb remotely…….

Scientists invent electronic skin that gives amputees sense of touch
E-skin delivers pleasurable and painful sensations to brain through temperature, pressure and strain sensors